Accounting is one of the key functions of almost all businesses. Whether you work with a bookkeeper or an accountant, a strong knowledge of accounting basics can help you better manage your business finances and meet tax obligations.
The accrual method of accounting allows you to record income as it is earned, rather than when it is received. This can make it easier to create financial forecasts and estimates for budgets.
Basics of Accounting
Accounting is the process of systematically recording and reporting financial transactions, and it is also known as the “language of business.” It is necessary to generate reports that communicate important financial information to both internal and external users. This information is used to make decisions, gain perspective and assess performance. Accounting also helps to prevent fraud and error.
It is a systematic way of recording and communicating financial information about a business’s assets, liabilities and operations. It is used to report the results of a company’s activities and is based on generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). It includes recording events, classifying them in an account and summarizing them in profit and loss accounts and balance sheets. It is also necessary to communicate the results in a clear and concise manner.
There are a number of different accounting methods that can be used, depending on the needs of a particular business. For example, cash-basis accounting is the simplest method, which stipulates that a transaction should only be recorded when there is actual receipt or payment. In contrast, accrual accounting requires that a sale is recorded when it occurs, even if the customer has not paid yet.
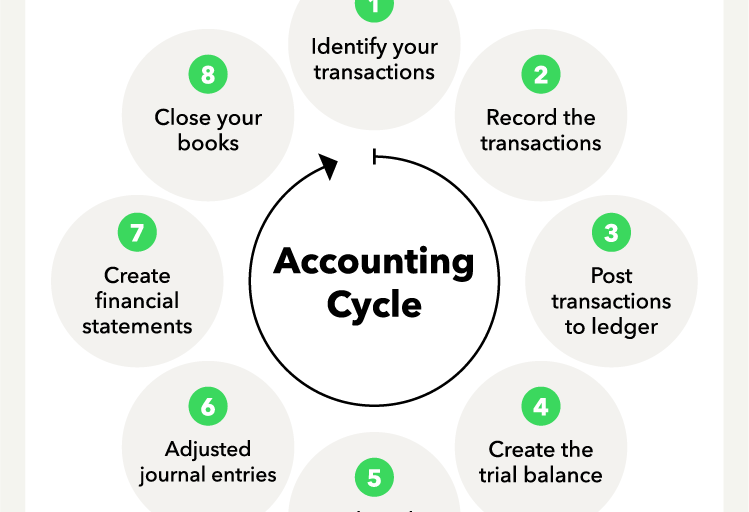
To keep track of a company’s transactions, accountants use a chart of accounts, which is a list of all the accounts that are tracked in an organization. Each time a transaction takes place, it is recorded in the accounting system by creating a journal entry for each item. Then the entries are summarized in a general ledger, which is then reconciled to other documents, such as bank statements or receipts.
Another step is closing the books, which is a process that takes place at the end of an accounting period. It involves adjusting entries made during the period, as well as transferring the net profit from income and expense accounts to equity accounts, such as retained earnings or capital. It is also necessary to prepare a variety of reports, such as an aging report, which lists customers’ accounts receivable and their due dates, and a cash flow statement.
Financial Statements
Financial statements are curated records that present an accurate, realistic summary of a company’s work for a set period. These are a key tool for internal management processes, such as business analysis and budgeting, but they also serve as the primary information package for external conversations with lenders, investors and compliance agencies. They must be produced consistently to avoid delays and costly misinterpretations. Financial statements include a balance sheet, income statement and cash flow statement.
A balance sheet shows what a company owns and owes at a fixed point in time, an income statement illustrates how much money it made or lost during a specific period and a cash flow statement highlights the inflows and outflows of funds over that same period. Companies must create more than one statement to showcase all aspects of their financial performance, because no single report tells the entire story.
There are many different formats and conventions that exist for creating financial reports, but most public companies must adhere to either Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United States or International Financial Reporting Standards for countries outside the United States. These standards dictate the underlying methods for record-keeping, data collection and reporting that allow these statements to be comparable over time and between competitors.
An understanding of the fundamental concepts and principles behind financial accounting opens up a world of insights, opportunities and perspective for business owners and managers. It also makes it easier to proactively mitigate risk and efficiently prioritize projects to achieve big goals.
An ability to read and understand financial statements is a crucial skill for aspiring entrepreneurs, finance specialists and business professionals at all levels. These are documents that reveal the financial health of a business, and they can make or break a deal or investment opportunity. Fortunately, flexible accounting software has replaced leather-bound ledgers and seven-column spreadsheets to handle the task of producing and publishing these important documents for both private and public businesses. These programs allow small businesses to automate and streamline this process for maximum efficiency.
Taxes
There are some differences between accounting methods that impact a company’s taxation situation. The method chosen affects how financial reports are used for filing taxes and claiming tax deductions. The right method can also help a business determine its long-term profitability based on current true income. Some of the methods may even increase the chances of obtaining debt financing or improving a business’s evaluation by investors and other financial institutions.
Depending on what type of business you operate, you may be required to use a particular accounting method. This is because the Internal Revenue Service has rules about how and when you should report expenses and income. The IRS considers a business’s taxable income to be the net profit after all costs of operations have been deducted. This includes the cost of goods sold, shipping and manufacturing costs. It also includes any credits to customers such as a credit memo or merchandise return.
The Internal Revenue Service allows taxpayers to use either the cash or accrual accounting method to figure taxable income for a given tax year. However, the methods must be consistent and clearly reflect income. If a company wants to change its accounting method, it must receive permission from the IRS to do so.
The IRS publishes several publications that explain special methods of accounting for certain types of income or expenses. These methods often differ from generally accepted accounting principles, so taxpayers should consult this publication to determine whether their chosen method meets IRS requirements. To avoid being penalized for a wrong accounting method, taxpayers should carefully evaluate their choices and be prepared to defend their selections. The IRS can impose significant penalties on businesses that don’t follow proper accounting procedures.
Payroll
Payroll is one of the most complex and time-consuming parts of accounting. It involves calculating and distributing employee wages while withholding taxes, deductions and other expenses. It also includes generating various reports that comply with tax laws and regulations. The process of running payroll is highly reliant on the accuracy of records and calculations, and even the smallest errors can result in costly penalties. This is why it is so important for businesses to use a payroll system that eliminates errors and helps businesses stay in compliance.
There are many different systems to choose from when it comes to payroll management, and the best option depends on your business’s needs and budget. A system that is integrated into your accounting software can save you time and money by reducing the number of steps it takes to process each payment. It will also make it easier for you to track your business’s accounting and payroll data.
A good payroll system will enable you to manage employee information, track overtime hours, calculate and record deductions and statutory payments (such as EPF, ESI and TDS) as well as maintain a database of past payslips for each employee. It will also enable you to create a variety of reports for your business and tax agencies, such as payroll registers, payment summaries and year-end statements.
While a manual method is fine for small businesses with few employees, it becomes inefficient and error-prone as your company grows. To avoid costly mistakes, it is recommended that you use a computerized payroll system. This way, you can be sure that your employees are being paid correctly and on time.
The type of payroll system you choose will depend on the type of accounting you use. Cash basis accounting requires you to record income and expenses as soon as they are received, whereas accrual accounting allows you to record revenue and expense amounts based on the work performed rather than when they are actually paid. Some companies use a hybrid method that combines the benefits of both cash and accrual accounting.
The chart of accounts is a set of financial accounts that record the transactions and balances that your company makes. These include assets, liabilities and equity. Examples of liabilities are accounts payable and receivable, while the equity accounts include the owner’s equity and stockholders’ equity accounts.